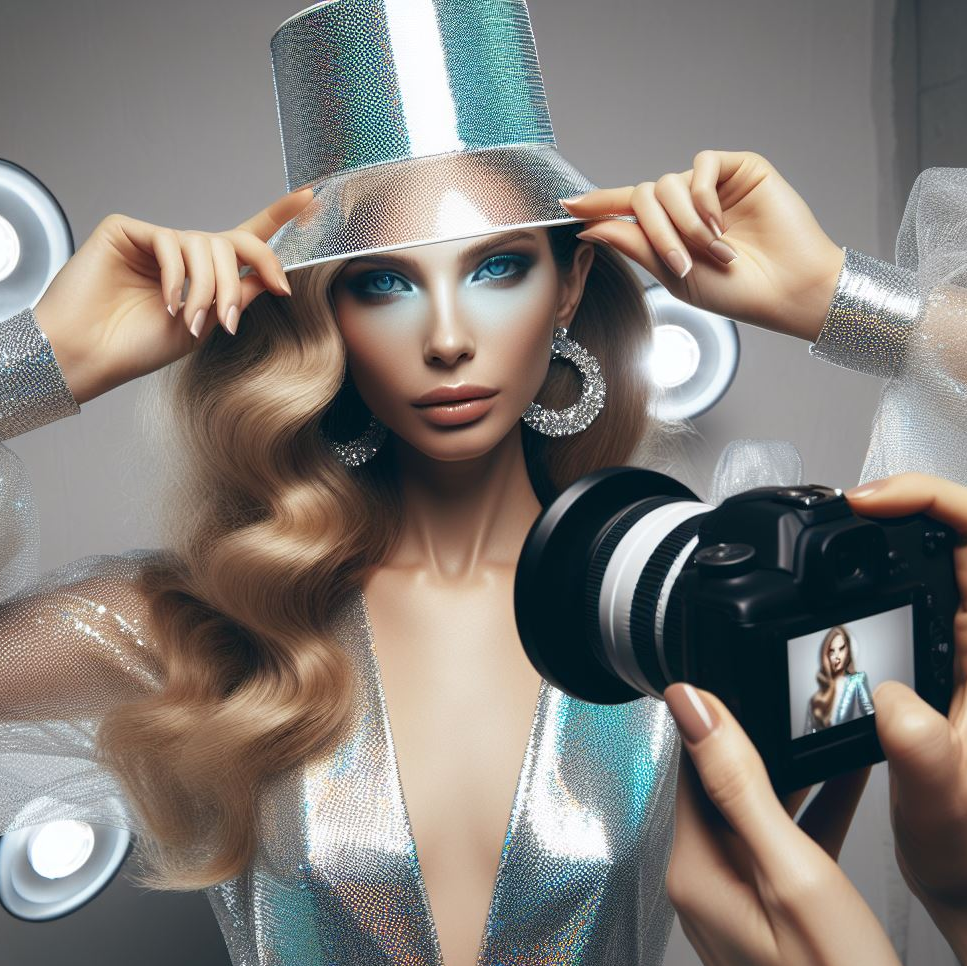
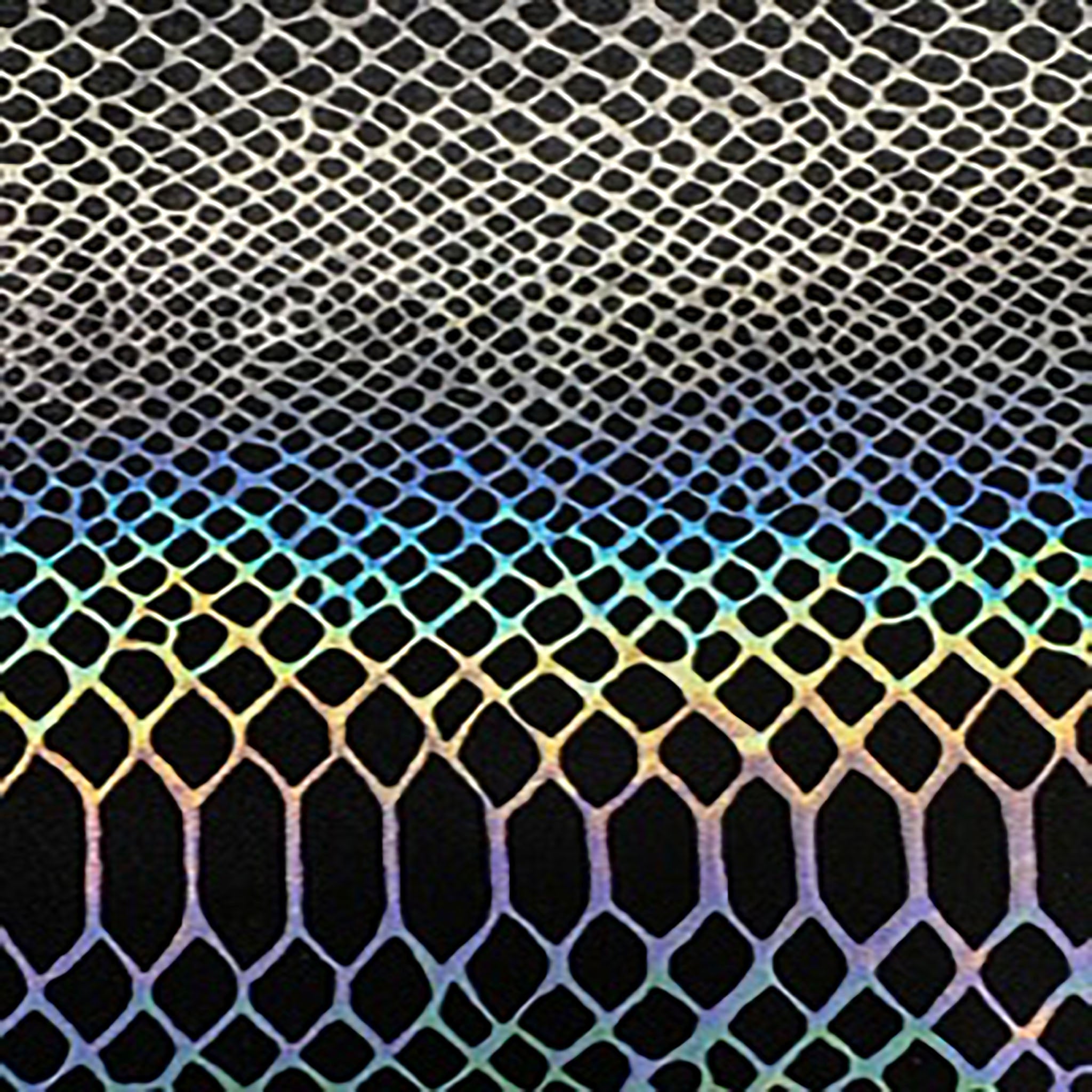
Holographic materials are nothing short of mesmerizing, captivating our imagination with their unique properties and dazzling visual effects. At Spandex Palace, we delve into the science and allure of holographic material to understand its magic.
How it Works: The Basics of Holography
-
Light Interference: At the heart of holography lies the principle of light interference. Unlike traditional photography, which captures only intensity and color, holography records both the amplitude and phase of light waves. This allows holographic material to recreate a three-dimensional image that appears almost lifelike.
-
Laser Precision: The process begins with a laser beam splitting into two—one directed at the object being recorded, and the other at a reference beam. The light waves from these beams interact with each other on the holographic material's photosensitive surface.
-
Capturing the Interference Pattern: As the two beams converge on the holographic plate or film, they create an interference pattern. This pattern, a result of the varying phases of light waves, is a unique imprint of the object. It's this intricate interference pattern that gives holograms their depth and realism.
-
Reconstruction: When illuminated by a coherent light source, such as another laser or a specific wavelength of light, the holographic material recreates the recorded interference pattern. This process reconstructs the original object in three dimensions, allowing viewers to see it from different angles as they move around.

Important Properties of Holographic Material
-
High Resolution: Holographic materials boast exceptional resolution, capturing intricate details with precision. This high level of detail is crucial for producing lifelike holographic images.
-
Angle Sensitivity: Holograms are angle-sensitive, meaning the viewing angle affects what the observer sees. This property adds to the dynamic nature of holographic displays, offering different perspectives based on the viewer's position.
-
Color Purity: Unlike traditional photographs, holographic materials can reproduce colors with remarkable accuracy. The interference pattern captures the full spectrum of light, resulting in vibrant and true-to-life holographic images.

-
Thickness Matters: The thickness of the holographic material influences the colors produced. Thin materials tend to create a rainbow-like effect, while thicker ones exhibit a more pronounced and vibrant color spectrum.
-
Durability and Stability: Holographic materials need to be stable and durable to preserve the integrity of the recorded holograms. Factors such as resistance to environmental conditions and longevity are crucial for maintaining the quality of holographic displays.
-
Versatility: Holographic materials are versatile and can be applied to various substrates, including films, plates, and even fabrics. This adaptability makes holographic material suitable for a wide range of applications, from security features on credit cards to eye-catching fashion statements.